Page 1
Unit 4
Electricity
Name:________________________________________ Pd:____
Page 2
Unit 4: Electricity
Vocab
1. Static ________________________________________________________________________
Electricity
________________________________________________________________________
2. Static ________________________________________________________________________
Discharge
________________________________________________________________________
3. Potential ________________________________________________________________________
Difference
________________________________________________________________________
4. Voltage ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
5. Voltage ________________________________________________________________________
Source
________________________________________________________________________
6. Ohm’s Law ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
7. Series ________________________________________________________________________
Circuit
________________________________________________________________________
8. Parallel ________________________________________________________________________
Circuit
________________________________________________________________________
9. Grounded ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
10. Short ________________________________________________________________________
Circuit
________________________________________________________________________
Page 3
11. Battery ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
12. Alternating ________________________________________________________________________
Current
________________________________________________________________________
13. Direct ________________________________________________________________________
Current
________________________________________________________________________
14. Electronics ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
15. Electronic ________________________________________________________________________
Signal
________________________________________________________________________
16. Analog ________________________________________________________________________
Signal
________________________________________________________________________
17. Digital ________________________________________________________________________
Signal
________________________________________________________________________
18. Diode ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
19. Transistor ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
20. Integrated ________________________________________________________________________
Circuit
________________________________________________________________________
21. Binary System ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________

Page 4
Unit 4: Electricity
In-Class Notes
Objective 4.01: Know the cause and effect of static electrical charges
Interactions between charges
• Like Charges ________________________
• Picture:
• Opposite Charges ________________________
• Picture:
Static Electricity
• Buildup of charge on an object creates ___________________________________________
• ____________________________________________________________
• Static discharge - _____________________________________________________________________________________________
• Examples:
o _________________________________
o _________________________________
o _________________________________

Page 5
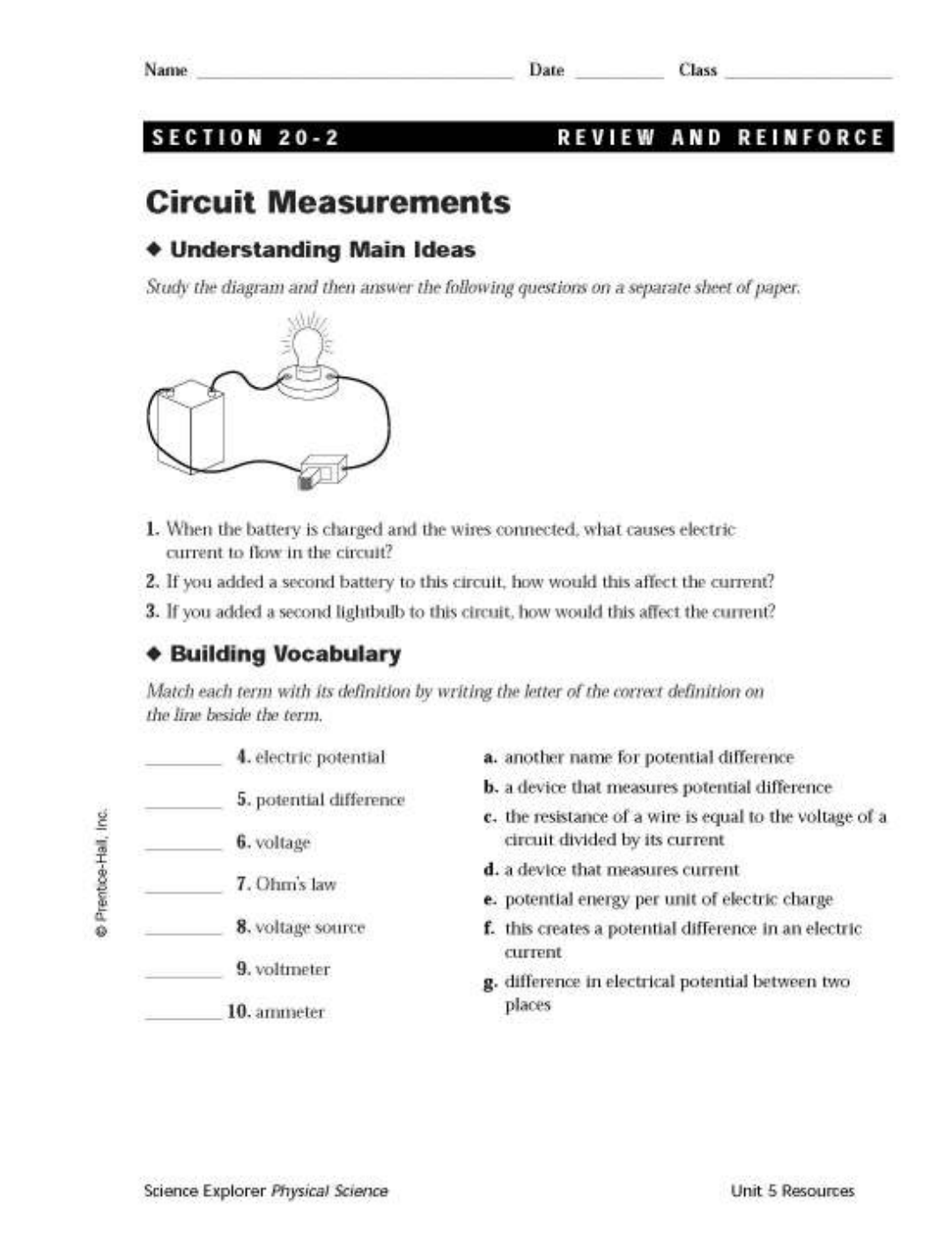
Objective 4.02: Apply concepts of voltage, current, and resistance
Current
• _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
o Units: _________________________
(shortened to ________________________ which means _________ mA = ___ A)
o Electrical Potential: _________________________________________________________________________________
o Voltage/ Potential Difference: _____________________________________________________________________
Units: _________________
o Voltage Source: ______________________________________________________________________________________
o Resistance: ___________________________________________________________________________________________
Units: ________________
Symbol: ______________
Three Requirements for Current Electricity:
(1) __________________________________________________________ ________________________________
(2) __________________________________________________________ ________________________________
(3) __________________________________________________________ ________________________________
Ohm’s Law
• Equation: ___________________
o V = Voltage = _________________________
o I = Current = _________________________
o R = Resistance = __________________________________________________
V = IR
Symbol Unit
Voltage
Current
Resistance
Page 6
Sample Problem #1
An automobile headlight is connected to a 12 V battery. If the current is 0.40 A, find the resistance.
Sample Problem #2
Find the voltage needed to run a waffle iron if the current required is 12 A and the resistance is 10 Ω.
Objective 4.03: Identify circuit symbols on an electrical circuit diagram
Circuit Symbols
Name Symbol
Battery
Resistor
Switch
Ground
Bulb
Sample Circuit
Page 7
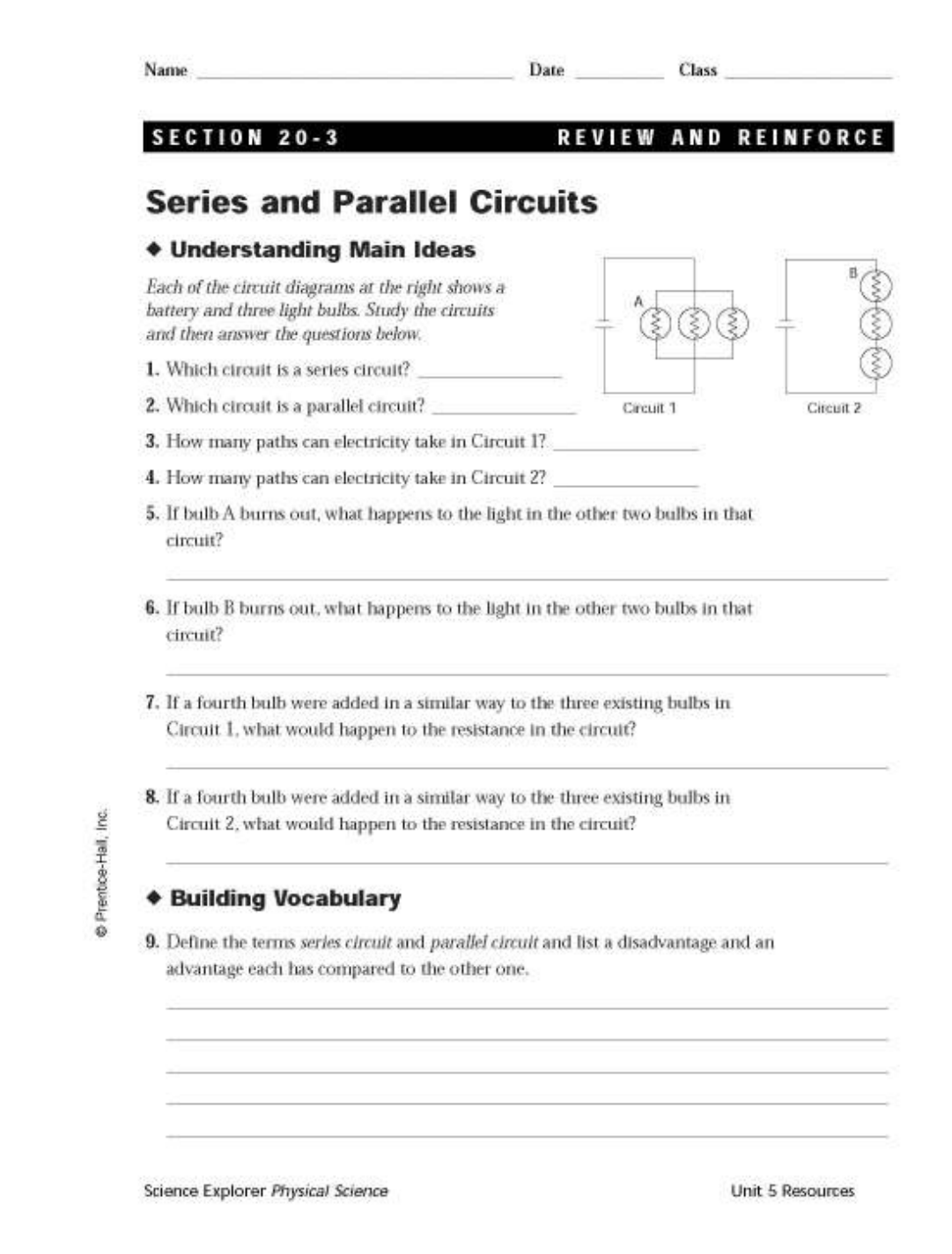
Objective 4.04: Distinguish between series and parallel circuits
4.05: Describe different arrangements of cells, resistors, lamps, and switches in electric
circuits
Series vs. Parallel Circuits
Series Parallel
Definition
Picture
Advantages
Disadvantages
Objective 4.06: Compare and contrast direct and alternating current
Direct Current
• ________________________________________________________________________________
• Examples:_________________________________
Alternating Current
• ________________________________________________________________________________
• Examples:_________________________________
• Explanation:
Page 8
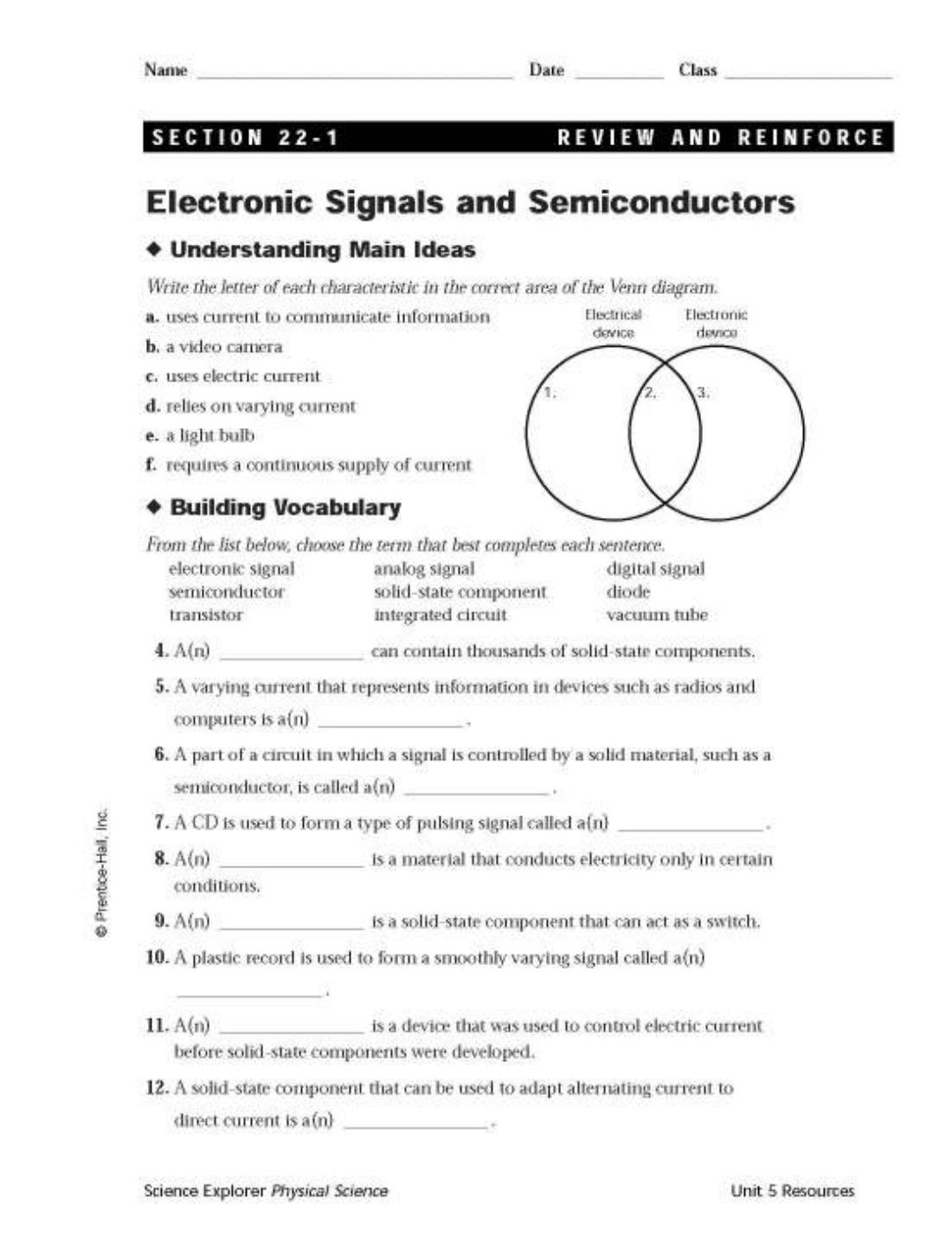
Objective 4.07: Define and compare digital and analog signals
What is electronics?
• _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
• Electronic signal: ____________________________________________________________________________________________
Analog vs. Digital Signals
Analog Digital
Definition
Example
Objective 4.08: Describe the use of semiconductors in electronics
Semiconductors
• _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
• Examples of Semiconductors:
• Diode – ______________________________________________________________________________________________
• Transistor –_________________________________________________________________________________________
• Integrated Circuit – __________________________________________________________________________________
Page 9
Objectives 4.09: Explain how telephones, televisions, and radios transmit and receive signals
4.10: Explain the difference between AM and FM radio signals
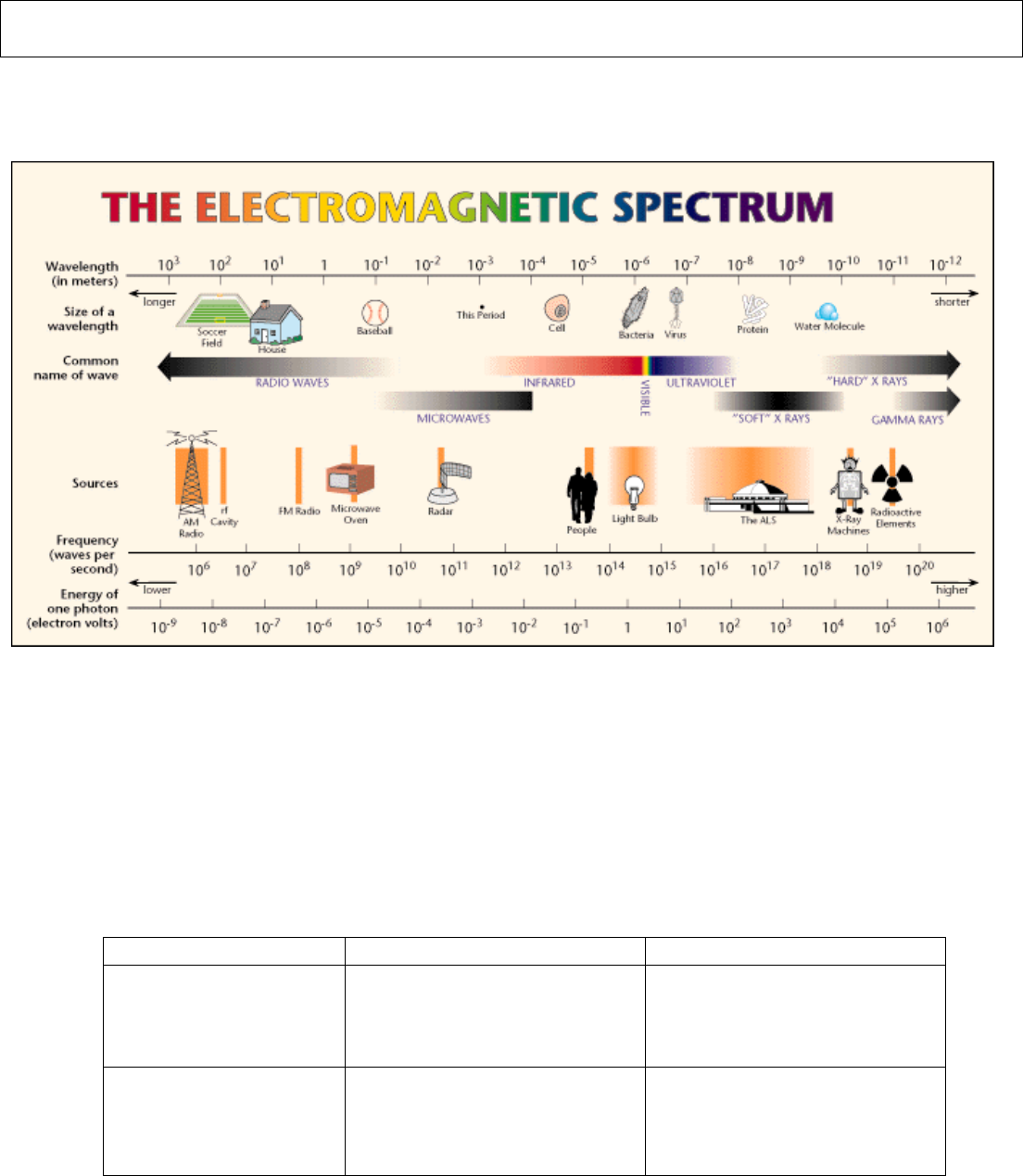
The Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum
• EM Waves allow for:_______________________________________________________________________________________
Electronic Communication
• Telephones
o Transmitter:_______________________________________________________________________________________
o Receiver: __________________________________________________________________________________________
• Radios
AM Radio FM Radio
What it Stands For
How it Works
Page 10
Page 11
Page 12

Page 13
Unit 4: Electricity Review
Modified True/False
Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement
true.
____ 1. For a constant voltage, increasing the resistance will cause the current to decrease. _________________________
____ 2. In a parallel circuit, there is only one path for current to take. _________________________
____ 3. If one light bulb is removed from a parallel circuit with three bulbs, the brightness of the other bulbs will decrease.
_________________________
Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 4. The charge on a proton is
a
negative, and the charge on an electron is positive.
b
positive, and the charge on an electron is negative.
c
the same as the charge on an electron.
d
.
can change according to the situation.
____ 5. As in the case of like magnetic poles, like electric charges
a
attract each other.
b
repel each other.
c
exist in pairs.
d
.
do not interact.
____ 6. The buildup of charges on an object is called
a
static discharge.
b
static electricity.
c
positive charge.
d
.
negative charge.
____ 7. The loss of static electricity as electric charges move off an object is called
a
friction.
b
conduction.
c
induction.
d
.
static discharge.
____ 8. An example of a voltage source is a(n)
a
electrical wire.
b
battery.
c
electric circuit.
d
magnet.
____ 9. According to Ohm’s law, what is the resistance of a light if the voltage is 9.0 volts and the current is 0.30 amps?
a
0.033 ohms.
b
2.7 ohms.
c
30 ohms.
d
.
8.7 ohms.
Page 14
____ 10. In a series circuit with three bulbs,
a
there are many paths for the current to take.
b
the remaining two bulbs are not affected if one bulb burns out.
c
all of the bulbs become dimmer as more bulbs are added.
d
.
a switch is never used.
____ 11. In a parallel circuit with three bulbs,
a
the bulbs must all be located on the same branch.
b
there is only one path for the current to take.
c
current from each bulb has its own path through the circuit.
d
.
the overall resistance increases if a new branch is added.
____ 12. A connection that allows current to take an unintended path is called a
a
short circuit.
b
series circuit.
c
parallel circuit.
d
.
grounded circuit.
____ 13. When charges are able to flow directly from the circuit into the ground connection, the circuit is electrically
a
exposed.
b
grounded.
c
shorted.
d
.
shocking.
____ 14. The type of current produced by a battery is
a
direct current.
b
alternating current.
c
magnetic current.
d
.
induced current.
____ 15. The symbol for current is
a
C.
b
I.
c
P.
d
V.
_____16. Which of the following is an example of an analog signal?
a. compact disc
b. record player
c. computer hard drive
d. dvd
_____17. The use of electricity to control, communicate, or process information is called:
a. transistor
b. superconductor
c. am radio
d. electronics
_____18. Which of the following is not an example of a semiconductor?
a. amplitudicator
b. diode
c. integrated circuit
d. transistor
Page 15
_____19. The ______ Spectrum shows how electronic signals are carried over long distances.
a. FM
b. AM
c. EM
d. PM
_____20. Which part of the telephone converts sound into an electronic signal?
a. transmitter
b. phone cord
c. receiver
d. buttons
_____21. AM Radio is short for:
a. all modulation
b. amplitude modification
c. amplitude modulation
d. always modulated
_____22. FM Radio is short for:
a. fine-tuned modification
b. frequency modulation
c. frequency modification
d. four type modulation
_____23. The binary system uses what two numbers to represent information?
a. 5 and 3
b. 0 and 5
c. 0 and 1
d. 0 and 10
_____24. A semiconductor is a material that conducts current ___________________ than insulators, but
________________ than conductors.
a. worse, better
b. better, worse
c. faster, slower
d. slower, faster
_____25. The semiconductor that allows current to flow in only one direction is called a ___________.
a. transistor
b. integrated circuit
c. modulator
d. diode
Page 16
Short Answer
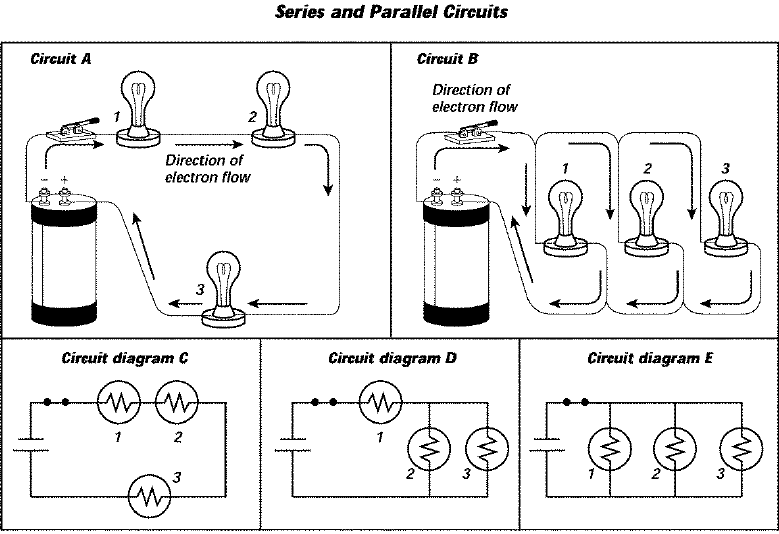
26. Which circuit—A or B—represents a series circuit? Explain your answer.
27. Which circuit—A or B—is a parallel circuit? Explain your answer.
28. Which circuit diagram represents circuit B?
29. What will happen to bulb 1 in circuit A if the switch is opened?
30. Will removing bulb 1 in circuit B cause bulb 3 to go out? Explain.
31. What will happen to bulb 2 in circuit diagram D if bulb 1 burns out?
